BMA
The Bond Market Association, see SIFMA below.
Cap
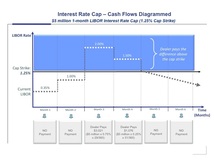
Caps are similar to insurance against interest rates rising above a predetermined level of protection, referred to as the "strike". If rates rise above the strike, the portion of the rate increase above the strike is reimbursed to the hedger. Caps are sold by dealers to hedgers through an up front premium. See Cap Cash Flow Diagram.
Collar
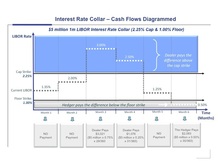
A combination of a Cap and a Floor. Collars are typically done in lieu of purchasing a Cap alone, as the Floor is sold by the hedger to the dealer in order to reduce the up front premium cost of the Cap.
See Collar Cash Flow Diagram.
Confirmation
See ISDA Master Agreement below.
Convexity
Credit Support Annex (CSA)
See ISDA Master Agreement below.
Day Count
The convention applied to determine the number of days, and which days, to include in an interest calculation. The three most common Day Count conventions are 30/360, Actual/360, and Actual/365, but many others are used throughout the various financial markets.
- In a 30/360 day count (a.k.a. "bond" basis), it is assumed each month has 30 days in a 360-day year, or an even 1/12.
- In an Actual/360 day count (a.k.a. "Act/360" or "money market" or just "money" basis), the actual number of days is applied over a 360-day year. US Dollar LIBOR is on an Actual/360 basis.
- In the case of Actual/365 (a.k.a. "Act/365" or "Treasury" basis) the actual number of days is applied over a 365-day year.
DV01
In-the-money
Floor
ISDA
The International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) is a trade organization of participants in the market for over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives. It is headquartered in New York, and has created a standardized contract (the ISDA Master Agreement, see below) to enter into derivatives transactions. ISDA also creates industry standards for derivatives and provides legal definitions of terms and procedures used in derivative contracts. See the ISDA website.
ISDA Master Agreement
The ISDA Master Agreement is typically used between a derivatives dealer and their counterparty when discussions begin surrounding a derivatives trade. There are two basic forms of Master Agreement: single jurisdiction/currency and multiple jurisdiction/currency. One of these documents is generally combined with a Schedule to set out the basic trading terms between the parties. The terms of the Schedule are often negotiated. Each subsequent trade is then recorded in a Confirmation which references the Master Agreement and Schedule. The ISDA Master Agreement was first published in 1992, and a second edition was published in 2002.
Possibly the most important aspect of the ISDA Master Agreement is that the Master Agreement and all the Confirmations entered into under it form a single agreement. This is very important as it allows the parties to an ISDA Master Agreement to aggregate the amounts owing by each of them under all of the Transactions outstanding and replace them with a single net amount payable by one party to the other.
In addition to an ISDA Master Agreement and Schedule, (along with a Confirmation for every trade), derivative counterparties may also choose to enter into a Credit Support Annex (CSA) which further permits parties to mitigate their mutual credit risk by requiring the party which is "out-of-the-money" to post collateral, usually in the form of cash, government securities or highly rated bonds). The amount of collateral posted is negotiated, but typically corresponds to the amount which would be payable by that party if all the outstanding Transactions under the relevant ISDA Master Agreement were terminated.
Possibly the most important aspect of the ISDA Master Agreement is that the Master Agreement and all the Confirmations entered into under it form a single agreement. This is very important as it allows the parties to an ISDA Master Agreement to aggregate the amounts owing by each of them under all of the Transactions outstanding and replace them with a single net amount payable by one party to the other.
In addition to an ISDA Master Agreement and Schedule, (along with a Confirmation for every trade), derivative counterparties may also choose to enter into a Credit Support Annex (CSA) which further permits parties to mitigate their mutual credit risk by requiring the party which is "out-of-the-money" to post collateral, usually in the form of cash, government securities or highly rated bonds). The amount of collateral posted is negotiated, but typically corresponds to the amount which would be payable by that party if all the outstanding Transactions under the relevant ISDA Master Agreement were terminated.
LIBOR
LIBOR, or the London Interbank Offering Rate, ...
Lost Decade
The Lost Decade (失われた10年 Ushinawareta Jūnen) is the time after the Japanese asset price bubble's collapse within the Japanese economy, which occurred gradually rather than catastrophically. It consists of the years 1991 to 2000. See Wikipedia Article.
Mark-to-market
Master Agreement
See ISDA Master Agreement above.
Out-of-the-money
PV01
SIFMA
The Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association, formerly known as the Bond Market Associaton, or BMA. See the SIFMA website.
Yield Curve
A line that plots the interest rates, at a set point in time, of bonds having equal credit quality, but differing maturity dates. The most frequently reported yield curve compares the various maturities of U.S. Treasury debt. See Investopedia.
ZIRP
A "zero interest rate policy". This is a monetary tool used by central banks to stimulate economic growth by making the cost of financing as low as possibly, or in fact a zero percent (0%) nominal interest rate. See Wikipedia.